Have you ever saw when you enter into Windows to enhance your storage drives, it states retrim for SSDs? Simply exactly what is getting trimmed and why is it required? Is it the like defragmenting or something completely various? (it is various).
Such great concerns all should have extensive responses, so in this short article we’ll cover all of that.
What is SSD cutting?
SSD cutting is a procedure that assists to preserve the efficiency of a solid-state drive in time. Cut works by occasionally removing blocks of information that are no longer in usage. The cut information isn’t constantly gotten rid of quickly, as a complicated procedure chooses precisely when this happens. However when it does, not just does it maximize area on the drive, it assists the SSD carry out much better and last longer, too.
Simple, yes? What really goes on, though, is a fair bit more complicated– keep reading to discover!
Going into the guts of your SSD
To comprehend why SSDs do not simply erase files when you push the button, we require to take a glimpse at how they work. We have actually taken apart SSDs prior to and you’ll see that there’s very little within them.
The sample listed below is of a fairly old SATA design (Samsung 850 Pro), however even the current SSDs aren’t much various in regards to the parts that comprise the drive.
The chip in the middle is a processor that handles all the directions, information circulation, file encryption, and other algorithms. Above it is a percentage of DRAM, which functions as a guideline and information cache, plus it keeps a table of information areas on the drive.

To the right and listed below the processor are 2 NAND flash modules– these are the chips that keep all of the information and it’s them that we require to look into.
Deep inside these chips are billions of small parts, called charge-trapping floating-gate metal oxide semiconductor field impact transistors Because that name does not precisely roll off the tongue, the innovation is generally called charge trap flash (CTF) and is the most typically utilized system to keep information in today’s SSDs.
Each CTF functions as a single system of storage, called a memory or bit cell, that has 3 electrical traces linked to it. The CTFs are organized together, initially as a long column (a string), with anywhere in between 32 and 128 cells.
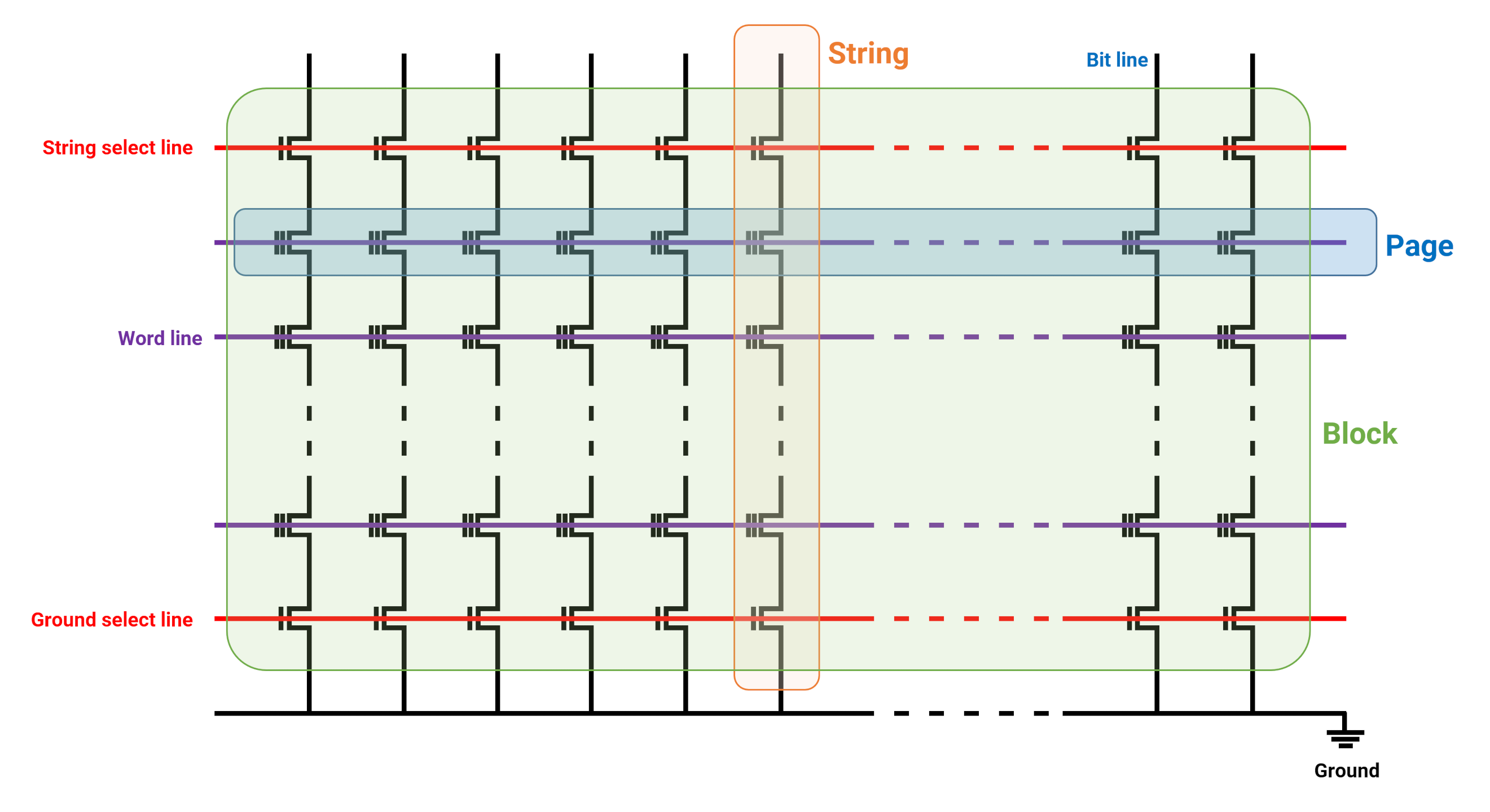
The cells in a string share a typical trace (a bit line), which is utilized to check out the information saved in them. Those that are on the exact same row as each other (called a page) are all linked to another typical trace (word line). The string and ground choose lines are utilized in mix with the word lines to figure out whether a read, compose, or remove procedure happens.
A variety of strings and pages forms what is called a block Pages and obstruct sizes differ tremendously, with the previous being as little as 4 kB in size, and the latter as big as 512 kB, although a lot depends upon the producer and design.
A single NAND flash pass away will make up countless blocks, and flash modules themselves might consist of several passes away. These large, complicated grids of traces and transistors comprise every flash storage gadget, from USB memory sticks worth a couple of dollars, to enterprise-level multi-terabyte SSDs.
NAND flash is odd
Pages and blocks are essential since all of the memory cells in this structure share the exact same substrate– the piece of semiconducting product, such as silicon or gallium arsenide, that all of the transistors are built on.
To remove information from any cell includes using a high unfavorable voltage, requiring any electrons saved in the CFT to stream into the substrate. Sadly, this implies that the remove procedure wipes tidy every cell in the block, not simply among them.
Another curiosity with NAND flash is that the memory cells can not be configured with brand-new information till all of the cells have actually been wiped tidy– to put it simply, SSDs never ever straight compose brand-new information over old things, which conventional hard disk drives do. And where removing needs to be done at the block level, composing to them is done at the page level, which implies that configuring an SSD is much faster than removing one.
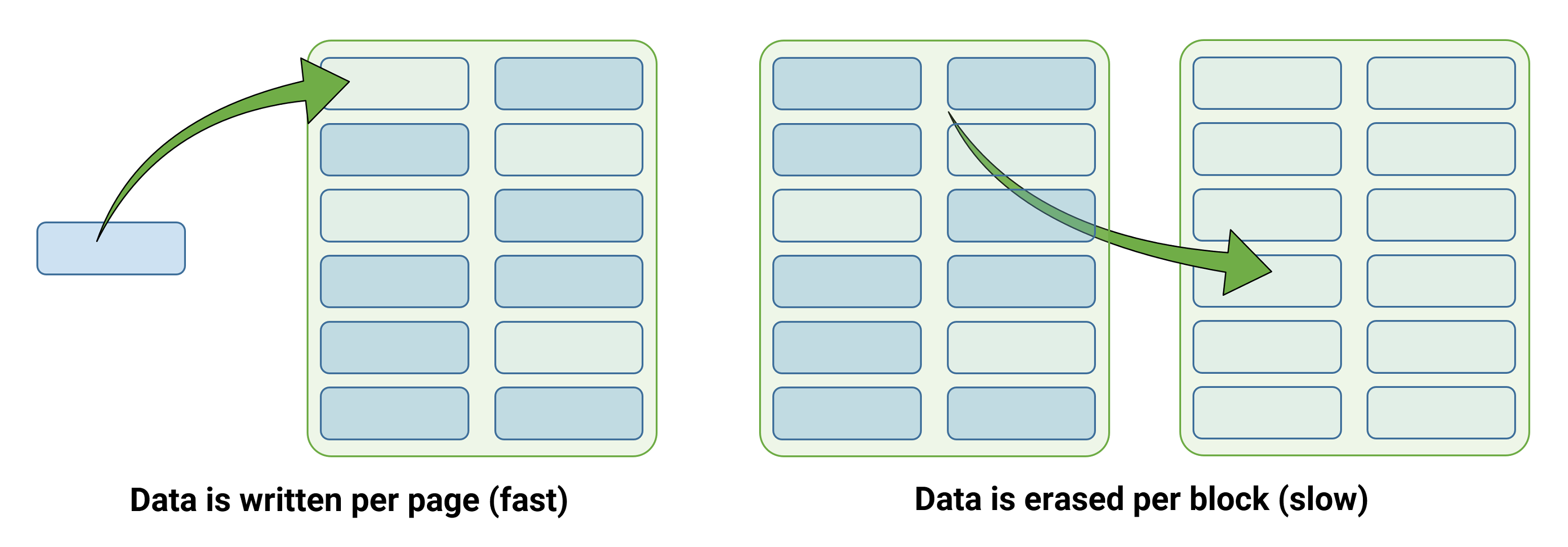
The procedure of programs and removing likewise harms the memory cells each time, deteriorating the layer inside the transistor that keeps the charge. To enhance the durability of the chips, the processor handling them cycles through all of the blocks, till every one has actually been utilized when, prior to returning to the start (so to speak).
So yes, NAND flash is certainly odd– quick composes, sluggish erases, damages itself doing either operation!
Tossing around the trash
Now, let’s return to comprehending what SSD cutting is everything about. To do this, we’ll take a fictional SSD that has 4 kB pages and 256 kB blocks, so 64 pages per block. What would take place if you wished to erase a file that uses up 3056 kB on your SSD?
This file will be using up 764 pages– 11 complete blocks and one with 60 out of the 64 pages utilized. How do we erase this file without running the risk of impacting those last 4 pages, as they could be consisting of information for another file? Looks like we’re entirely stuck!
Rescue at first can be found in the type of the TRIM command. All information remains on the storage drive till it is clearly advised to do something about it. Files and folders that have actually been erased by the os are flagged as no longer being needed, and when the TRIM command is released, the table saved in the SSD’s DRAM (or the NAND flash itself, if the drive does not have any DRAM) is then upgraded to show this.
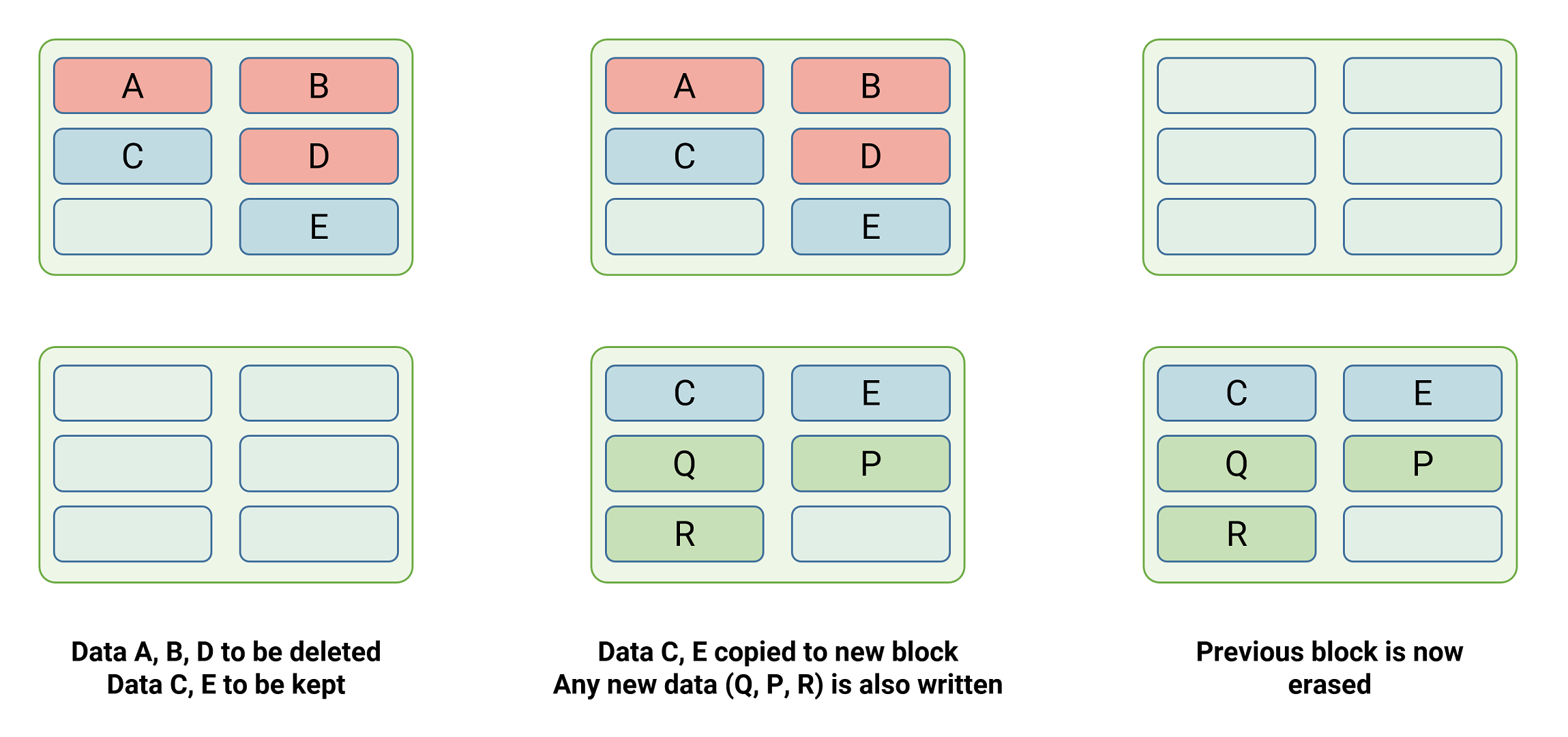
Keep In Mind that not every SSD producer utilizes the term TRIM however Windows does, so we’ll adhere to utilizing this term. Information isn’t eliminated instantly after the TRIM command has actually been sent out– it either happens when the drive is idle or when it next composes some information to a block. Which technique gets utilized depends upon the producer, with consumer-grade designs managing eliminates when idle, and enterprise-level ones typically doing it when composing.
Information that are flagged for elimination are eliminated when the NAND flash’s firmware starts a procedure called trash collection This includes checking out a block and any pages that require to be kept are copied to the cache, then composed to a completely empty block. The previous one, in addition to the pages flagged for removal, is then eliminated.
In some methods, this procedure is to SSDs what disk defragmentation is to conventional hard disk drives, however it’s not the exact same thing.
Is trim the like defragmenting?
SSD cutting and defragmenting are not the exact same thing. Defragmenting is a procedure that is utilized to enhance the efficiency of disk drive (HDDs) by reorganizing the information on the disk so that it is saved in an adjoining way. This enhances the effectiveness of the drive by minimizing the quantity of time it requires to check out and compose information.
On the other hand, Cutting specifies to SSDs and is utilized to preserve the efficiency of the drive in time. SSDs utilize of flash memory implies they have a restricted variety of compose cycles. When information is erased from an SSD, the area that it inhabited is not instantly offered for reuse. Rather, the drive’s firmware marks the area as “void” and it is not overwritten till the Cutting procedure is carried out. This procedure assists to avoid the drive from ending up being fragmented and decreasing.
Trash collection is helpful to the life-span of the SSD and its total efficiency, and TRIM simply makes it much better (in some cases the 2 terms are utilized interchangeably). This is since without that command, trash collection will simply continuously move all pages about, condensing partly filled blocks, to keep newly eliminated blocks readily available for programs– however this implies undesirable pages will get moved about too, losing time and increasing the wear on the memory cells. Due to the fact that TRIM clearly mentions which pages are now scrap, they can be left alone throughout trash collection and eliminated as needed.
Sending the clippers
TRIM is immediately released by Windows when you completely erase a file (i.e. eliminate it from the Recycling Bin) however it does not quickly occur. It’s contributed to a line and gets processed when the SSD is prepared for it.
Nevertheless, this line has an optimum size to it, and if it gets filled, a few of those TRIM demands will get dropped. By default, Windows schedules a re-issue of TRIM commands regularly (calling it a retrim).
You can require this to occur however we do not advise you do so. However if you firmly insist, go to Submit Explorer, right-click on a drive, click Characteristics, and after that on the Tool tab. Lastly, click the button that states Enhance If you do not have any SSDs in your PC, enhancing simply runs typical disk defragmentation, however for NAND flash gadgets, clicking this re-issues a TRIM command. You can’t really make the drive to do anything, so do not stress over running it too often; the drive will care for itself completely well!
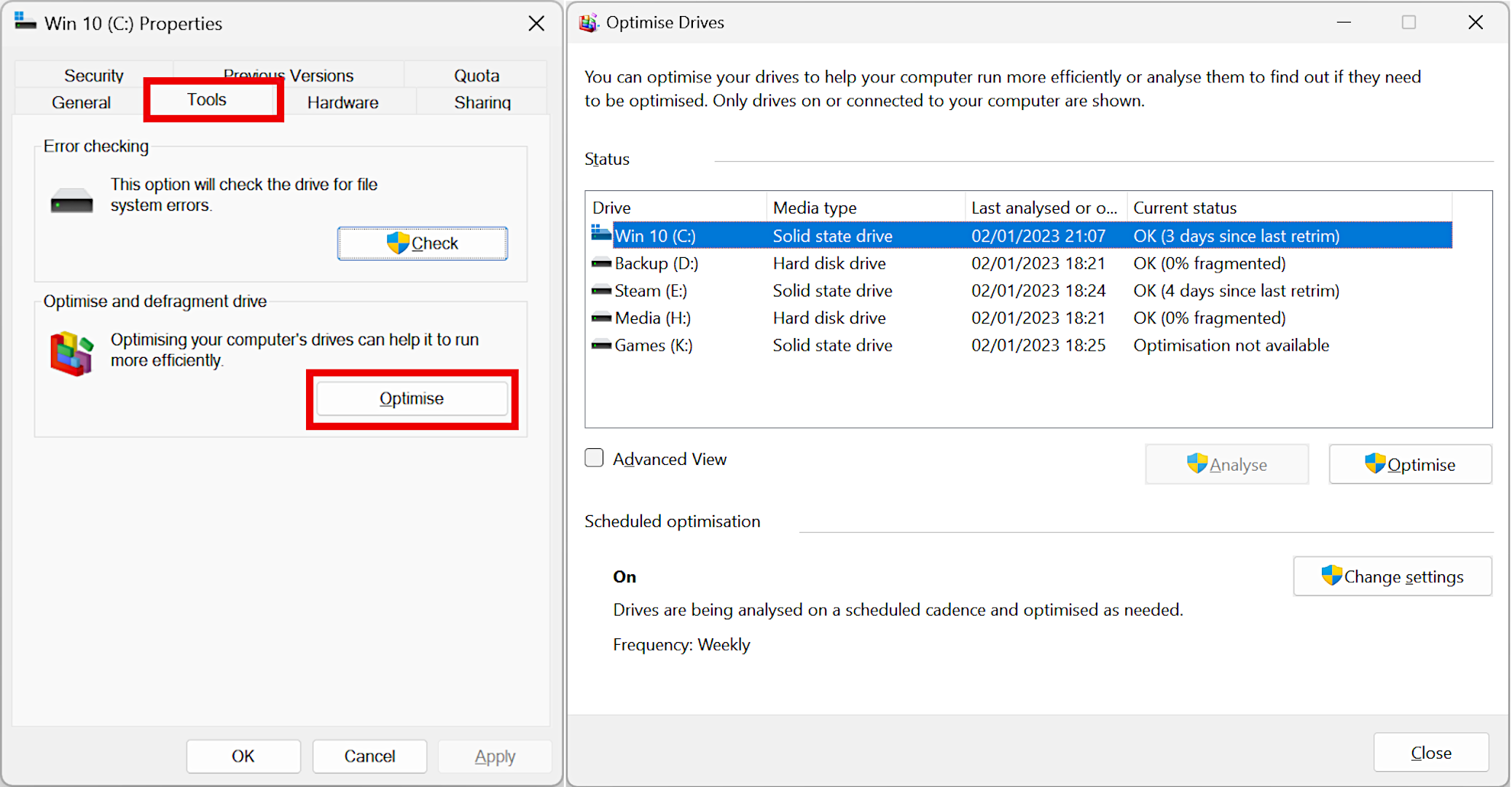
See how among the SSDs above can’t be enhanced? That’s since it’s utilizing a dynamic volume, which does not support using cutting. Standard volumes do acknowledge the TRIM command and for many users, it’s finest to utilize that kind of drive volume anyhow.
If your os or SSD setup does not support TRIM, it’s not actually problem– trash collection still happens, however the procedure isn’t anywhere near as efficient. Old information ultimately gets gotten rid of just since the drive will ultimately overwrite undesirable pages, eventually in time.
For PCs utilizing Windows 7, TRIM is just supported on SATA SSDs; for devices with NVMe ones, the command is just readily available in Windows 8, 10, and 11. TRIM was contributed to MacOS in the last upgrade to Snow Leopard back in 2011. A lot of Linux circulations likewise support the operation, however not every file system works– speaking of which, RAID systems typically do not support TRIM, although that circumstance is gradually enhancing.
Now you understand what TRIM is and how it’s helpful to your SSD.




